Overheating is a critical concern in LED displays, impacting performance, longevity, and user experience. Effective heat dissipation design is essential to maintain optimal functioning and avoid premature failures. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how to control LED display temperatures effectively, enhance efficiency, and ensure long-lasting performance.
Why Heat Dissipation Matters in LED Displays?
LED displays, especially in outdoor and high-brightness applications, generate significant heat. Without proper management, overheating can lead to:
Reduced Lifespan: Prolonged exposure to heat degrades LEDs, power supplies, and other components.
Color Shifting: Heat affects color consistency, causing variations that impact display quality.
Efficiency Loss: Overheating can lead to decreased brightness and efficiency, affecting visual performance.
Safety Risks: Excessive temperatures could lead to burns, fires, or malfunctions, posing a hazard.
By designing a system with efficient heat dissipation, you can protect your LED displays from these potential issues.

Principles of Heat Dissipation Design for LED Displays
Heat dissipation is achieved through three main mechanisms:
Conduction: Direct transfer of heat from one part of the system to another.
Convection: Heat transfer through air or fluid movement.
Radiation: Emission of heat from the LED surface to its surroundings.
A good design incorporates all three mechanisms, ensuring efficient cooling of the entire display structure.
Effective Cooling Techniques for LED Displays
Several cooling techniques can be implemented based on display size, application, and environment:
a) Passive Cooling (Convection)
Heat Sinks: Metal fins or plates attached to LEDs and other components draw heat away, releasing it into the air.
Thermal Conductive Materials: Materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum and copper, are ideal for managing heat dissipation.
b) Active Cooling (Forced Convection)
Fans: Fans create airflow, helping remove heat from high-temperature zones. This method is effective but requires maintenance and power.
Liquid Cooling: For extremely high-power applications, liquid cooling systems circulate coolant to absorb and transfer heat away from components.
c) Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Thermal Paste or Pads: Placed between components, TIMs improve the transfer of heat between surfaces, maximizing conduction efficiency.

Advanced Technologies in LED Display Heat Management
As LED technology advances, so do cooling solutions. Some modern methods include:
Phase Change Materials (PCMs): PCMs absorb heat by changing states (solid to liquid), effectively managing temperature spikes.
Graphene Coatings: Graphene is highly thermally conductive, and adding a graphene layer on surfaces can improve heat dissipation.
Design Considerations for Optimal Heat Dissipation
When designing LED displays, consider the following:
Ambient Environment: Displays in outdoor or sunny locations will face higher temperatures and require more robust cooling systems.
Component Layout: Proper spacing between LEDs, resistors, and power supplies prevents heat buildup.
Airflow Optimization: Ensure ample airflow within the display housing for natural or forced convection to be effective.
Power Supply Location: Keeping power supplies away from high-temperature zones reduces overall heat and potential stress on LED components.
Monitoring and Maintenance for Consistent Heat Dissipation
Even the best designs need regular monitoring. Implement temperature sensors within the display to alert operators if overheating occurs. Regular cleaning of fans, checking for wear on thermal pads, and verifying airflow channels will ensure the system continues to operate efficiently.

The Benefits of Effective Heat Dissipation Design
With a robust heat dissipation strategy, LED displays benefit from:
Extended Lifespan: Proper heat management prolongs the life of LEDs and other critical components.
Improved Performance: Stable temperatures maintain color consistency, brightness, and energy efficiency.
Reduced Operational Costs: Efficient cooling minimizes energy use, lowering operating costs over time.
Enhanced Safety: Reduced risk of overheating decreases the chances of accidents and equipment damage.
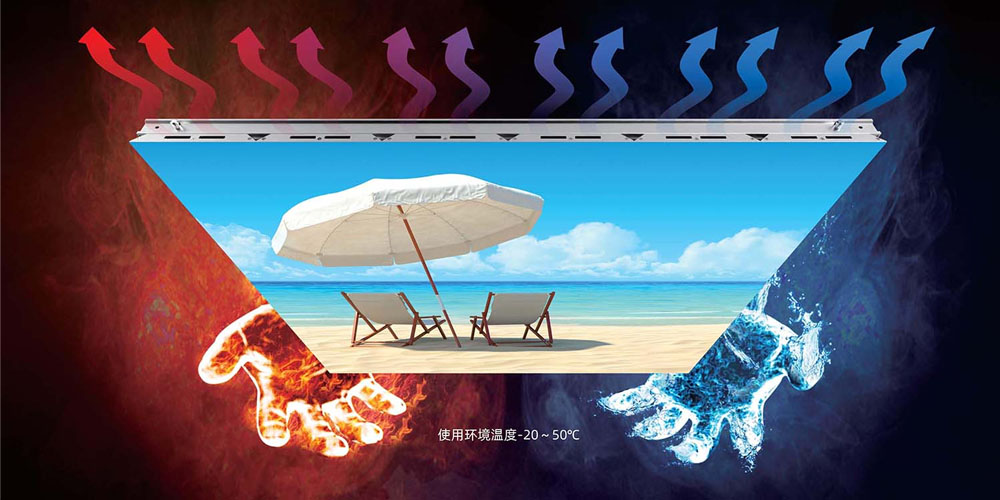

Conclusion
Effective heat dissipation design is essential for reliable, long-lasting LED display performance. By understanding and applying the principles and techniques outlined here, you can protect your investment, optimize performance, and ensure your displays remain vivid and safe. Say goodbye to overheating worries—design a heat dissipation system that keeps your LEDs cool and efficient.



